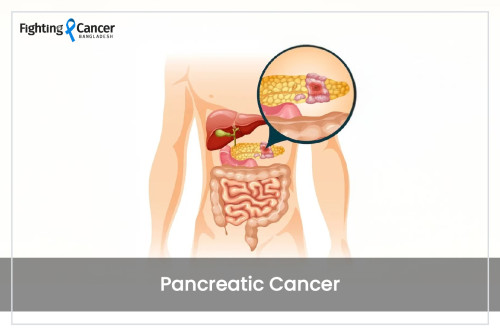
When abnormal cells start to grow and proliferate in the pancreas, it is termed pancreatic cancer. The most common pancreatic cancer is pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. This is a gland located in the lower abdomen and behind the stomach.
The pancreas plays a vital role in our body. It produces enzymes that help to digest food and hormones that manage our body’s blood sugar.
Statistics
Pancreatic cancer is the 12th most common cancer in the world. Pancreatic cancer is mostly found over the age of 65 and rarely found below the age of 40. The average lifetime risk of developing this cancer is 1 in 56 in men and about 1 in 60 in women.
Risk factors and symptoms
- Direct and indirect smoking
- Diabetes (type II)
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Family history
- Obesity
- Consumption of alcohol
- Aging
Most people with pancreatic cancer do not have any early symptoms, they start to appear at the advanced stage. Common symptoms include jaundice, dark urine, light-colored stool, itchy skin, pain in the belly or back, stomach ulcers, pain, loss of appetite, nausea, tiredness, weight loss, diarrhea, and symptoms of diabetes.
Prevention
Unfortunately, pancreatic cancer cannot be prevented. However, we can reduce the rate of cancer by limiting exposure to the risk factors. We should maintain a healthy weight and avoid smoking and consumption of alcohol.
Treatment
The survival rate of pancreatic cancer is very low. However if it is detected at an early stage, it could be cured with proper treatment. Treatment depends on some factors, like the location of the tumor, its stage, the patient’s health condition, and whether it is spread or not.
If cancer is confined inside the pancreas, surgery is recommended to remove all of the cancer. Other methods used to treat pancreatic cancer are chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy.

