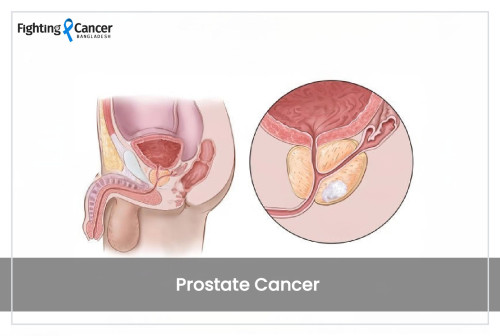
The prostate is a tiny walnut-fashioned gland in the pelvis of men, that produces the seminal fluid that nurtures and carries sperm. The cancer cells form within the tissues of the prostate. It is one of the most common kinds of non-skin cancer and the second leading cause of death due to cancer in American men. Although many prostate cancers grow slowly and are confined to the prostate gland, some types of prostate cancer are aggressive and can spread swiftly through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to nearby organs, such as the bladder and bones.
Statistics
Older men and non-Hispanic Black men are more susceptible. The average age is 50-65 or older, but it is rare in men under 40. The American Cancer Society reports about 248,530 new cases of prostate cancer and around 34,130 deaths from prostate Cancer in 2021.
Risk Factors And Symptoms
Factors that can increase your risk of prostate cancer include:
- Older age (above 65)
- Race (non-Hispanic Black)
- Family history of prostate cancer or breast cancer (BRCA1 or BRCA2) genes
- Hormonal imbalance
- Unhealthy diet
- Obesity
- Smoking
Symptoms include painful urination, decreased urine flow, blood in urine, blood in semen, pain in bones, weight loss, and erectile dysfunction.
Prevention
The risk of prostate cancer can be reduced with a healthy diet, lifestyle change, exercise, healthy weight maintenance, and doctor-prescribed medications. Regular screening for prostate cancer is inevitable for early therapeutic intervention.
Several research studies have documented the use of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, such as finasteride (Propecia, Proscar) and dutasteride (Avodart), to downgrade the risk of developing prostate enlargement leading to cancer.
Treatment
Treatment for prostate cancer depends on the disease progression. Chemotherapy (Docetaxel, Cabazitaxel, Mitoxantrone, Estramustine), radiation therapy, immunotherapy (Sipuleucel-T vaccine, PD-1 inhibitor); cryotherapy, hormone therapy (LHRH antagonists, orchiectomy), targeted therapy (PARP inhibitors), and surgery (open prostatectomy, Laparoscopic prostatectomy, Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) are the current treatment options.

