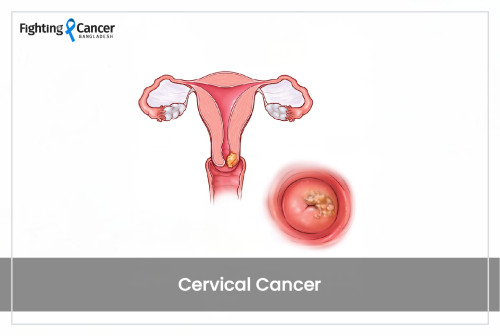
Cervical cancer initiates in the lower portion of the uterus called the cervix. The cervix attaches the lower part of the uterus to the vagina and forms the birth canal. Cervical cancer develops on the surface of the cervix; if seen in the vagina, it is called the ectocervix, or in the canal, it is called the endocervix.
There are 2 main types of cervical cancer: squamous cell carcinoma, which is the majority (80% to 90%) of all cervical cancers and starts on the outer surface covering of the cervix, and adenocarcinoma (10% to 20%), which starts in the glandular cells that line the lower birth canal in the internal portion of the cervix.
Statistics
An estimated 14,480 women will be diagnosed with invasive cervical cancer. Hispanic women and Black women are more susceptible. An estimated 4,290 deaths from cervical cancer will occur this year.
Risk Factors And Symptoms
The factors that are most likely inclined towards the incidence of cervical cancer are
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Immune system deficiency
- Herpes
- Smoking
- Age (above 30)
- Lower socioeconomic status
- Race (Black women, Hispanic women, American Indian women)
- Use of oral contraceptives
- Exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES)
Symptoms include blood spots or light bleeding between or following periods, longer, heavier menstrual bleeding, bleeding after intercourse, douching, or a pelvic examination, increased vaginal discharge, pain during sexual intercourse, bleeding after menopause, and unexplained, persistent pelvic and/or back pain.
Prevention
- Delaying first sexual intercourse until the late teens or older
- Avoiding sexual intercourse with multiple partners
- Avoiding sexual intercourse with someone who has had many partners
- Practicing safe sex, including condom use, although condoms cannot fully protect against HPV
- Having regular Pap tests to find and treat precancerous conditions
- Quit smoking
Treatment
Surgery (conization, LEEP, hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, radical trachelectomy, exenteration), chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiation therapy are the currently available treatment options.

