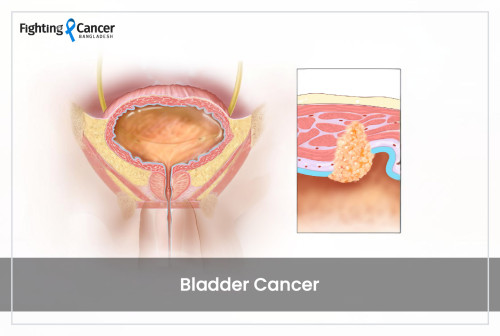
Bladder cancer begins in the cells that line the inside of the bladder. It is the fifth most common form of cancer and the fourth most common among men. The bladder lining urothelial cells are normally involved; they grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor.
Most urothelial carcinoma is non-muscle invasive and stays within the bladder’s inner lining. The other less common ones are squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and small cell carcinoma, which result in chronic irritation and inflammation. Benign bladder tumors are very rare. It typically affects people older than 70 and more often in men.
Statistics
83,730 adults (64,280 men and 19,450 women) have been estimated to be diagnosed with bladder cancer. Incidence rates in white men are double those of black men. The average age people are diagnosed with bladder cancer is 73. 17,200 deaths (12,260 men and 4,940 women) from this disease have been estimated. The 5-year survival rate for people with bladder cancer is 77%.
Risk Factors And Symptoms
Risk factors include
- Gender (men)
- Age (above 65)
- Tobacco use
- Smoking
- Race (white)
- Chemicals (textile, rubber, leather, dye, paint, and print industries; some naturally occurring chemicals; and chemicals called aromatic amine)
- Chronic bladder problems
- Cyclophosphamide use
- Pioglitazone (Actos) use
- Prior history
- Schistosomiasis
- Lynch syndrome and other genetic syndromes
- Arsenic exposure
Symptoms include blood or blood clots in the urine, pain or burning sensation during urination, frequent urination, flank pain, loss of appetite, weight loss, feeling the need to urinate many times throughout the night, feeling the need to urinate but not being able to pass urine, fatigue, and lower back pain on one side of the body.
Prevention
Abstain from smoking, reduce chemical exposure, and have a regular checkup if any of the risk factors are present.
Treatment
Surgery (transurethral bladder tumor resection (TURBT), radical cystectomy and lymph node dissection, urinary diversion), targeted therapy (Erdafitinib (Balversa), Enfortumab vedotin-ejfv (Padcev), chemotherapy (intravesical chemotherapy, systemic chemotherapy), immunotherapy (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG), interferon (Roferon-A, Intron A, Alferon), immune checkpoint inhibitors), and radiation therapy are the treatment options.

